

|
Ethernet connector and cable
Most ethernet networks use Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) cable. Category 5 (CAT5) cable widely used, but other variations are available. EIA/TIA specifies RJ-45 connectors - properly called 8P8C - (ISO 8877) for UTP (unshielded twisted pair) cable. (RJ45 refers to a set of connectors beyond the 8P8C standard but the former has replaced the latter in common usage).
Gigabit ethernet connector and cable
1000 BASE-T (also known as IEEE 802.3ab) is a standard for gigabit Ethernet over copper wiring. It requires, at least Category 5 cable (the same as 100 BASE-TX), but Category 5e (Category 5 enhanced) or Category 6 cable may also be used and are often recommended. 1000 BASE-T requires all four pairs to be present and is far less tolerant of poorly installed wiring than 100 BASE-TX.
Standard or straight-thru cable

Cross-over cable

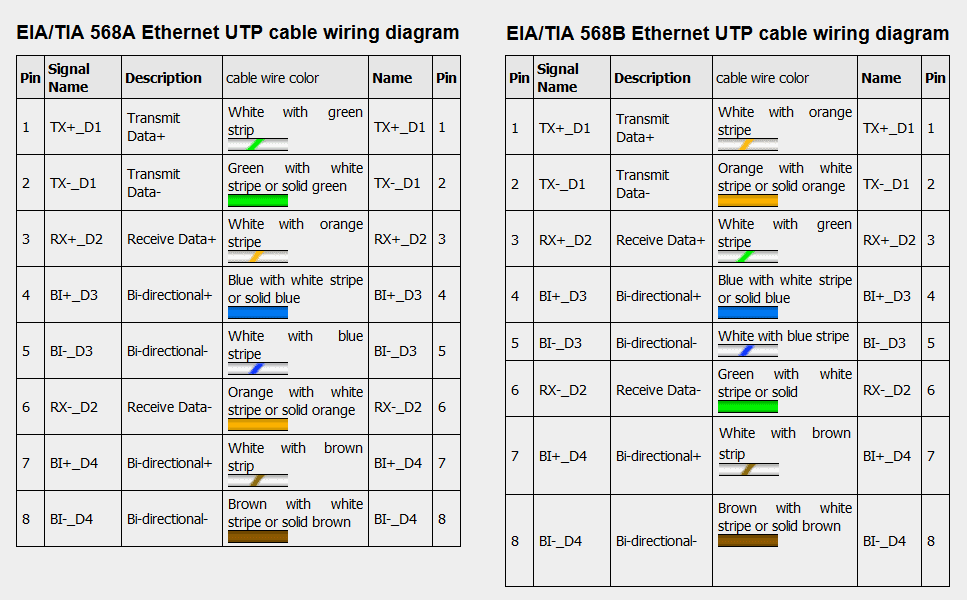
RJ45 ethernet pinout
There are two standards for network cable wiring: EIA/TIA 568A and EIA/TIA 568B.
Ethernet UTP cable length
Each network segment cable length may be up to 100 meters, although several chip manufacturers claim 150 meters. Autonegotiation is a requirement for using 1000BASE-T, according to the standard. Several device drivers will allow you to force 1000 Mbps full duplex to eliminate autonegotiation issues.
UTP network cabling history
Category 5 cable , commonly known as Cat 5, is an unshielded twisted pair cable type designed for high signal integrity. With the 2001 introduction of the TIA/EIA-568-B standard, the category 5 cabling specification was obsoleted and superseded by the category 5e specification.
The original specification for category 5 cable was defined in ANSI/TIA/EIA-568-A, with clarification in TSB-95. These documents specified performance characteristics and test requirements for frequencies of up to 100 MHz. Category 5 cable included four twisted pairs in a single cable jacket. It was most commonly used for 100Mbit/s networks, such as 100BASE-TX Ethernet, although IEEE 802.3ab defined standards for 1000BASE-T - gigabit Ethernet over category 5 cable. Cat 5 cable typically had three twists per inch of each twisted pair of 24 gauge copper wires within the cable. The twisting of the cable reduces electrical interference and crosstalk.
Cat 5e cable is an enhanced version of Cat 5 that adds specifications for far-end crosstalk, usually used for gigabit ethernet. Cat 5e cable does not enable longer cable distances for Ethernet networks: horizontal cables are still limited to a maximum of 90 m in length. Cat 5e cable performance characteristics and test methods are defined in TIA/EIA-568-B.2-2001.
The enhanced version Category 6a cable is defined at frequencies up to 500 MHz and needed to reach 10Gb/s with 10GBASE-T Ethernet.